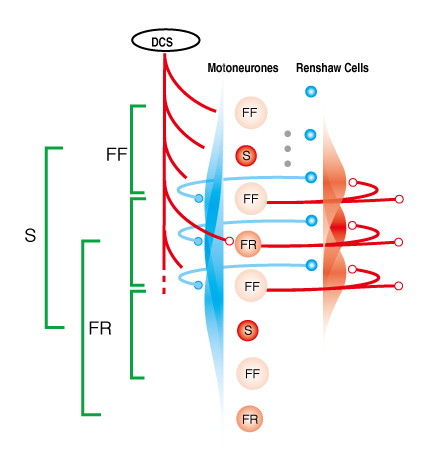
実際の筋に相当する数の運動単位(α運動ニューロンと筋線維)からなる神経回路網を構築して,生理学的知見に基づきながら,どのようなフィードバック系を構築すると,人に見られる運動特性を発現するようになるだろうか.反回抑制の神経回路網は,どのような役割をになっているのだろうか.
論文
- T. Uchiyama, U. Windhorst: ‘Effects of Spinal Recurrent Inhibition on Motoneuron Short-term Synchronization’, Biological Cybernetics, Vol. 96, No. 6, 561-575 (2007)
DOI: 10.1007/s00422-007-0151-7 - T. Uchiyama, H. Johannson. U. Windhorst: ‘Static and dynamic input-output relations of the feline medial gastrocnemius motoneuron-muscle system subjected to recurrent inhibition: a model study’, Biological Cybernetics, Vol. 89 No. 4, 264-273 (2003)
DOI: 10.1007/s00422-003-0417-7 - T. Uchiyama, H. Johannson. U. Windhorst: ‘A model of the feline medial gastrocnemius motoneuron-muscle system subjected to recurrent inhibition’, Biological Cybernetics, Vol. 89. No. 2, 139-151 (2003)
DOI: 10.1007/s00422-003-0413-y
発表
- 内山,U. Windhorst:「ネコの腓腹筋を支配する運動神経プールのモデル −Renshaw細胞による反回抑制とmotoneuronのsynchronization−」,第19回生体生理工学シンポジウム(2004).
- 内山,H. Johansson,U. Windhorst:「ネコの腓腹筋を支配する神経系の反回抑制モデル」,平成14年度電気学会 電子・情報・システム部門大会(2002).
- T. Uchiyama, U. Windhorst and H. Johannson: ‘Recurrent Inhibition Model of Cat Gastrocnemius Muscle’, Proc. 24th Ann. Conf. of IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (2002).
- T. Uchiyama and K. Akazawa: ‘Neural Network Model for Muscle Control Base on the Size Principle and Recurrent Inhivition of Renshaw Cells’, Proc. 1st Inter. Conf. on Atrificial Neural Networks in Medicine and Biology (2000).
- 内山,赤澤:「筋張力制御のための神経回路網モデルにおける レンショウ細胞とα運動神経細胞の結語数と発火パターン」,電子情報通 信 学会技術研究報告MEとバイオサイバネティスク (1999).
- 内山,赤澤:「運動単位の活動様式を模擬する筋張力制御のための神経回路網モデルの構築」 ,第16回バイオメカニズムシンポジウム (1999).
- 内山,赤澤:「サイズ原理とレンショウ細胞の抑制に基づく筋張力制御のための神経回路網モデル」,第14回生体生理工学シンポジウム (1999).
- T. Uchyama and K. Akazawa: ‘Force-Firing Rate Relation of Neural Network Model for Muscle Force Control’, Proc. 21st Ann. Conf. of IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (1999).
- 内山,赤澤:「レンショウ細胞による抑制とサイズ原理に基づく筋張力制御のニューラルネットワークモデル」,第12回日本ME学会秋季大会,1998年11月
- 内山,赤澤:「実際的な細胞数からなる筋張力制御のための神経回路網−抑制と筋張力の関係−」,第19回バイオメカニズム学術講演会,1998年11月
- T. Uchiyama and K. Akazawa: ‘Neural Network Model for Muscle Force Control based on the Size Principle and inhibition by Renshaw Cells’, Proc. 20th Ann. Conf. of IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (1998) .